Difference between revisions of "Surface Normals"
m (Nairnj moved page Multimaterial Normal Vector to Surface Normals without leaving a redirect) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Both [[Multimaterial MPM|multimaterial mode MPM]] and [[Crack Settings|explicit cracks]] need to calculate surface normals. These normals are a crucial step in accurate contact physics calculations. | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:NormalDef.jpg|right]] | |||
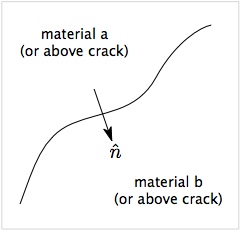
The surface normal is a key component of multimaterial mode MPM calculations. First, normals are needed to find the component of the velocity in the approaching direction, which is used to detect contact. Second, the normals are needed implement contact mechanics or [[Imperface Interfaces||imperfect interfaces]]. Practical experimental using multimaterial mode MPM simulations has revealed that accuracy of results is very sensitive to the method used to find the normals. | The surface normal is a key component of multimaterial mode MPM calculations. First, normals are needed to find the component of the velocity in the approaching direction, which is used to detect contact. Second, the normals are needed implement contact mechanics or [[Imperface Interfaces||imperfect interfaces]]. Practical experimental using multimaterial mode MPM simulations has revealed that accuracy of results is very sensitive to the method used to find the normals. | ||
== Normal Vector Options == | == Multimaterial Normal Vector Options == | ||
When multimaterial mode MPM was initially developed, contact was handled separately for each material's velocity field and the normal vector was found from that material's mass gradient. [[NairnMPM]] has implemented new methods that seem to work better. No one method works for all problems, which is why multiple options are available. This section describes the available options. | When multimaterial mode MPM was initially developed, contact was handled separately for each material's velocity field and the normal vector was found from that material's mass gradient. [[NairnMPM]] has implemented new methods that seem to work better. No one method works for all problems, which is why multiple options are available. This section describes the available options. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
Developer flags and maybe more options int he future | Developer flags and maybe more options int he future | ||
== Explicit Crack Normal Vector == | |||
Found from crack path and often more accurate the multimaterial mode such as for interfaces. | |||
Revision as of 08:49, 23 September 2013
Both multimaterial mode MPM and explicit cracks need to calculate surface normals. These normals are a crucial step in accurate contact physics calculations.
Introduction
The surface normal is a key component of multimaterial mode MPM calculations. First, normals are needed to find the component of the velocity in the approaching direction, which is used to detect contact. Second, the normals are needed implement contact mechanics or |imperfect interfaces. Practical experimental using multimaterial mode MPM simulations has revealed that accuracy of results is very sensitive to the method used to find the normals.
Multimaterial Normal Vector Options
When multimaterial mode MPM was initially developed, contact was handled separately for each material's velocity field and the normal vector was found from that material's mass gradient. NairnMPM has implemented new methods that seem to work better. No one method works for all problems, which is why multiple options are available. This section describes the available options.
Each Material's Gradient
Show picture two materials with two normals
Maximum Gradient
Show full vs partial
Average Gradient
Show top with two edges
Maximum Volume
Just describe
Custom Specified Normal
Developer flags and maybe more options int he future
Explicit Crack Normal Vector
Found from crack path and often more accurate the multimaterial mode such as for interfaces.