Element Types
This section lists the elements that can be used in FEA calculations
FEA Element Types
Solid Elements
The following solid elements are currently available in NairnFEA:
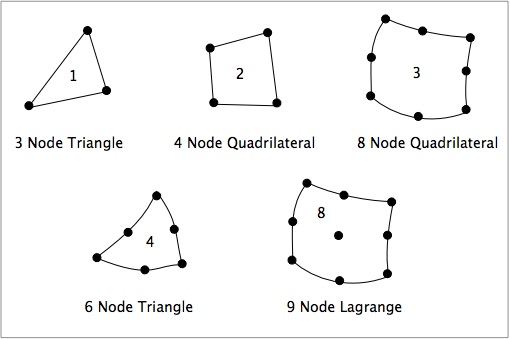
- 1 or "3 Node Triangle": 3-node constant-strain triangular elements (linear)
- 2 or "4 Node Quadrilateral": 4-node isoparametric rectangular elements (linear)
- 3 or "8 Node Quadrilateral": 8-node isoparametric rectangular elements (quadratic)
- 4 or "6 Node Triangle": 6-node isoparametric triangular elements (quadratic)
- 8 or "9 Node Lagrange": 9-node Langrangian rectangular element (quadratic) (9 point Gaussian quadrature)
These FEA element types are illustrated in the following figure. Note that imperfect interface elements are comprised of two separate paths with identical nodal coordinates and thus twice as many actual nodes as appear in the figure.
Interface Elements
The following interface elements are used to model imperfect interface:
- 5 or "4 Node Interface": 4-node imperfect interface elements (linear)
- 6 or "6 Node Interface": 6-node imperfect interface elements (quadratic)
These FEA element type are illustrated in the following figure. Note that imperfect interface elements are comprised of two separate paths with identical nodal coordinates and thus twice as many actual nodes as appear in the figure.
Scripted Input Files
In scripted input files, the element type is set using the Element command:
Element (elem)
where (elem) is a number or name from the above list. Once an element is selected, it remains the element used for all subsequent Area commands. If no Element command has be used, FEA calculations will default to "8 Node Quadrilateral" elements.
When using triangular elements (type 1 and 4), quadrilateral areas meshed using the Area Command first meshes the area into quadrilaterals and then creates triangular elements by dividing each quadrilaterals along its diagonal. To determine which diagonal in used, you can use the FlipTriangles command: into triangular elements.
The command to flip triangles is
FlipTriangles <(option)>
where (option) is yes or no to flip or not flip the triangles. This argument is optional. If it is omitted, the command will toggle the previous setting for triangle flipping. The initial value is always no.
This command takes effect when areas defined by four paths are meshed into trangular elements. Triangular elements are created by meshing the area in to quadrilaterals and then dividing each quadrilaterals along its diagonal. The flip triangles option determines which diagonal is used. Any new setting by a FlipTriangles command remains in effect until it is changed by another FlipTriangles command.
XML Input Files
In XML input files, the first <Area> block must define an element type in an attribute and refer to it by number from the above list. Subsequent <Area> blocks can omit the type attribute unless the element type is changed to have an analysis with mixed elements. For triangular elements, the diagonals are flipped using a flip attribute on the <Area> command instead of using a separate FlipTriangles command.
Notes
- When mixed elements are used, they must be compatible elements. In other words, you can mix linear elements (types 1, 2, and 5) with each other or quadratic elements (types 3, 4, 6, and 8) with each other, but cannot mix linear elements with quadratic elements in the same mesh.
- Solid (or quadrilateral) areas can only use solid elements (types 1, 2, 3, 4, and 8) while interface areas can use only inteface elements (type 5 and 6).