Trilinear Traction Law
The Traction Law
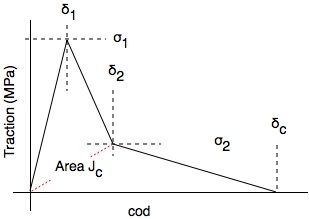
This traction law assumes a piece-wise linear relation with two arbitrarily-specifiable break points (i.e., three linear pieces). There are separate traction laws for opening displacement (mode I) and sliding displacement (mode II).
The toughness is
[math]\displaystyle{ J_c = {1\over2}\bigl(\sigma_1\delta_2 + \sigma_2(\delta_2-\delta_1)\bigr) }[/math]
The traction law for each mode depends up seven properties - (δ1,σ1) and (δ2,σ2) breakpoints, critical COD (δc), total area or toughness (Jc), and the initial elastic slope (k). You must enter exactly 5 of these seven properties for each mode. Furthermore, if one of the 5 is the initial slope, then either σ1 or δ1 for that mode (but not both) must be one of the five specified properties. The two remaining unspecified parameters will be calculated from the five provided parameters. The final law must satisfy δ1 ≤ δ2 ≤ δc, δc > 0, σ1 ≥ 0, σ2 ≥ 0, and σ1+σ2 & 0.
Failure
Traction Law Properties
The following properties are used to create a triangular traction law:
| Property | Description | Units | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| (other) | Properties common to all traction laws | varies | varies |