Difference between revisions of "Cubic Step Function Softening"
| (22 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
This [[Softening Laws|softening law]] was originally a step function (hence the name), but was latter generalized to allow it to be a cubic function that | == The Softening Law == | ||
This [[Softening Laws|softening law]] was originally a step function (hence the name), but was latter generalized to allow it to be a cubic function that can optionally rise to a peak before decaying to zero at <math>\delta_{max}</math>. The function is | |||
| | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
| | ||
<math>sG_c = \int_0^{\delta_{max}} f(\delta,s) = {\delta_{max}\over 2} \quad{\rm or}\quad \delta_{max} = 2sG_c</math> | <math>sG_c = \int_0^{\delta_{max}} f(\delta,s) = {\delta_{max}\over 2}\left(1+\frac{k}{6}\right) | ||
\quad{\rm or}\quad \delta_{max} = \frac{2sG_c}{k_6} \quad{\rm where}\quad k_6 = 1+\frac{k}{6}</math> | |||
Here ''s'' is the [[Softening Laws#Normalized Softening Law|softening scaling term]] and ''G<sub>c</sub>'' is toughness of the law | Here ''s'' is the [[Softening Laws#Normalized Softening Law|softening scaling term]] and ''G<sub>c</sub>'' is toughness of the law. | ||
The critical cracking strain, <math>\delta_{max}</math>, which depends on mesh size and crack orientation, is calculated from ''s'' and ''G<sub>c</sub>'' and is not a law property to be provided. | The critical cracking strain, <math>\delta_{max}</math>, which depends on mesh size and crack orientation, is calculated from ''s'' and ''G<sub>c</sub>'' and is not a law property to be provided. | ||
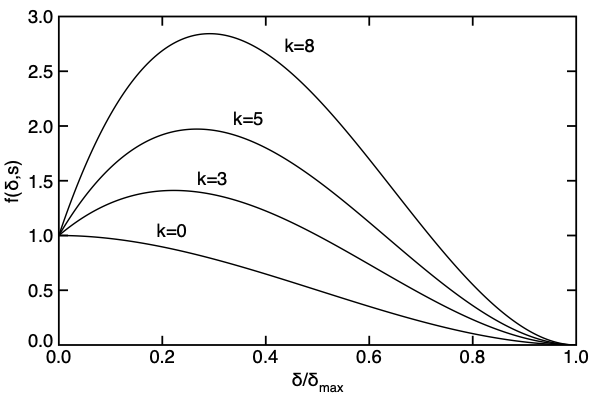
If <math>k=0</math>, this law is a cubic step function with <math>f'(0)=0</math>, but if <math>k | [[File:CubicStep.png|right]] | ||
If <math>k=0</math>, this law is a cubic step function with <math>f'(0)=0</math>, but if <math>k>0</math>, this function rises to a peak and then decays to failure at <math>\delta_{max}</math> (see plots on the right). This behavior is valid for softening laws provided the modulus still monotonically softens. When using <math>k>0</math>, you enter the initial stress into the [[Damage Initiation Laws|initiation law]]. If you want to set the peak stress, the initiation stress should be calculated from the desired peak using: | |||
| | ||
<math>\sigma_{0} = \frac{\left(1+\frac{k}{2}\right)^2}{\left(1+\frac{k}{ | <math>{\tt sigmac} = \sigma_{0} = \frac{\left(1+\frac{k}{2}\right)^2}{\left(1+\frac{k}{3}\right)^3}\sigma_{peak}</math> | ||
The area (or energy dissipation term) is | The area (or energy dissipation term) is | ||
| | ||
<math> | <math>\Omega(\delta,s) = {\delta \over 2} | ||
\left(1+\left({\delta\over \delta_{max}}\right)^2\left(\frac{4k_2-1}{3}-k_2{\delta\over \delta_{max}}\right)\right)</math> | |||
The stability | The stability factor is: | ||
| | ||
<math>\ | <math>\eta = \frac{12k_2}{(1+2k_2)^2k_6}</math> | ||
If <math>k=0</math>, the stability factor simplifies to <math>\eta = 4/3</math>, or slightly less stable than a [[Linear Softening|linear softening law]]. Although this stability factor goes to zero as <math>k</math> increases, the ''effective'' stability is better compared to monotonically decreasing laws by multiplying <math>\eta</math> by its peak value squared (''i.e.'', [[Softening Laws#Law Stability|minimum cell size]] is related to <math>\eta/\sigma_0^2</math> and <math>\sigma_0</math> decreases if set by scaling it from a fixed <math>\sigma_{peak}</math>). The ''effective'' stability of this law only decreases from 4/3 to 0.79 as <math>k</math> goes from zero to infinity. | |||
A difference between this law and [[Linear Softening|linear softening law]] is that <math>f'(\delta_{max})=0</math>. Thus, despite a reduction in stability, it is possible this zero derivative could reduce numerical effects caused by decohesions. | |||
== Softening Law Properties == | == Softening Law Properties == | ||
A cubic step function softening law as two parameters (only one is required): | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 41: | Line 48: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Gc || The toughness associated with the this softening law || [[ConsistentUnits Command#Legacy and Consistent Units|energy release units]] || none | | Gc || The toughness associated with the this softening law || [[ConsistentUnits Command#Legacy and Consistent Units|energy release units]] || none | ||
|- | |||
| k || Initial slope of the law (must be nonnegative) || none || 0 | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:00, 29 January 2023
The Softening Law
This softening law was originally a step function (hence the name), but was latter generalized to allow it to be a cubic function that can optionally rise to a peak before decaying to zero at [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{max} }[/math]. The function is
[math]\displaystyle{ f(\delta,s) = \left(1+2k_2{\delta\over \delta_{max} }\right)\left(1-{\delta\over \delta_{max} }\right)^2 \quad{\rm where}\quad k_2 = 1+\frac{k}{2} }[/math]
This cubic function has [math]\displaystyle{ f(0)=1 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ f'(0)= k/\delta_{max} }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ f(\delta_{max})=f'(\delta_{max})=0 }[/math]. The value for [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{max} }[/math] is found from
[math]\displaystyle{ sG_c = \int_0^{\delta_{max}} f(\delta,s) = {\delta_{max}\over 2}\left(1+\frac{k}{6}\right) \quad{\rm or}\quad \delta_{max} = \frac{2sG_c}{k_6} \quad{\rm where}\quad k_6 = 1+\frac{k}{6} }[/math]
Here s is the softening scaling term and Gc is toughness of the law. The critical cracking strain, [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{max} }[/math], which depends on mesh size and crack orientation, is calculated from s and Gc and is not a law property to be provided.
If [math]\displaystyle{ k=0 }[/math], this law is a cubic step function with [math]\displaystyle{ f'(0)=0 }[/math], but if [math]\displaystyle{ k\gt 0 }[/math], this function rises to a peak and then decays to failure at [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{max} }[/math] (see plots on the right). This behavior is valid for softening laws provided the modulus still monotonically softens. When using [math]\displaystyle{ k\gt 0 }[/math], you enter the initial stress into the initiation law. If you want to set the peak stress, the initiation stress should be calculated from the desired peak using:
[math]\displaystyle{ {\tt sigmac} = \sigma_{0} = \frac{\left(1+\frac{k}{2}\right)^2}{\left(1+\frac{k}{3}\right)^3}\sigma_{peak} }[/math]
The area (or energy dissipation term) is
[math]\displaystyle{ \Omega(\delta,s) = {\delta \over 2} \left(1+\left({\delta\over \delta_{max}}\right)^2\left(\frac{4k_2-1}{3}-k_2{\delta\over \delta_{max}}\right)\right) }[/math]
The stability factor is:
[math]\displaystyle{ \eta = \frac{12k_2}{(1+2k_2)^2k_6} }[/math]
If [math]\displaystyle{ k=0 }[/math], the stability factor simplifies to [math]\displaystyle{ \eta = 4/3 }[/math], or slightly less stable than a linear softening law. Although this stability factor goes to zero as [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] increases, the effective stability is better compared to monotonically decreasing laws by multiplying [math]\displaystyle{ \eta }[/math] by its peak value squared (i.e., minimum cell size is related to [math]\displaystyle{ \eta/\sigma_0^2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_0 }[/math] decreases if set by scaling it from a fixed [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_{peak} }[/math]). The effective stability of this law only decreases from 4/3 to 0.79 as [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] goes from zero to infinity.
A difference between this law and linear softening law is that [math]\displaystyle{ f'(\delta_{max})=0 }[/math]. Thus, despite a reduction in stability, it is possible this zero derivative could reduce numerical effects caused by decohesions.
Softening Law Properties
A cubic step function softening law as two parameters (only one is required):
| Property | Description | Units | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gc | The toughness associated with the this softening law | energy release units | none |
| k | Initial slope of the law (must be nonnegative) | none | 0 |