Difference between revisions of "Explicit FEA Cracks"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Explicit Cracks == | == Explicit Cracks == | ||
[[File: | [[File:Feacrack.jpg|right]] | ||
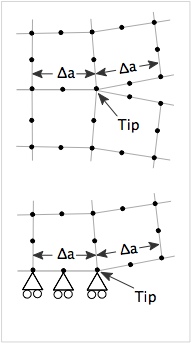
Cracks in FEA calculations are set up by configuring the mesh to include a crack. A crack can be internal to the mesh or, for symmetric loading, can be on an edge of the mesh and defined with the help of boundary conditions. These two crack geometries are illustrated on the right. In the first form, the two element edges to the right of the crack tip are initially aligned on the same coordinates. When the crack is loaded in tension, the edges separate and the point where they are joind is the crack tip. The static FEA run in [[NairnFEA]] does not include contact and therefore only opened crack can be modeled. | Cracks in FEA calculations are set up by configuring the mesh to include a crack. A crack can be internal to the mesh or, for symmetric loading, can be on an edge of the mesh and defined with the help of boundary conditions. These two crack geometries are illustrated on the right. In the first form, the two element edges to the right of the crack tip are initially aligned on the same coordinates. When the crack is loaded in tension, the edges separate and the point where they are joind is the crack tip. The static FEA run in [[NairnFEA]] does not include contact and therefore only opened crack can be modeled. | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 12 September 2013
FEA calculations can model explicit cracks.
Explicit Cracks
Cracks in FEA calculations are set up by configuring the mesh to include a crack. A crack can be internal to the mesh or, for symmetric loading, can be on an edge of the mesh and defined with the help of boundary conditions. These two crack geometries are illustrated on the right. In the first form, the two element edges to the right of the crack tip are initially aligned on the same coordinates. When the crack is loaded in tension, the edges separate and the point where they are joind is the crack tip. The static FEA run in NairnFEA does not include contact and therefore only opened crack can be modeled.
The second form of crack is for symmetric loading. The crack plane is on the bottom of the object and the displacement boundary conditions determine the location of the crack tip
The crack plane edges must be collinear and of equal length (Δa). When a calculation with cracks is done, the Crack Closure... command can be used to calculate crack tip energy release rate.