Difference between revisions of "Isotropic Material Failure Surface"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:FailureSurfacePlots.png|400px|right]] | [[File:FailureSurfacePlots.png|400px|right]] | ||
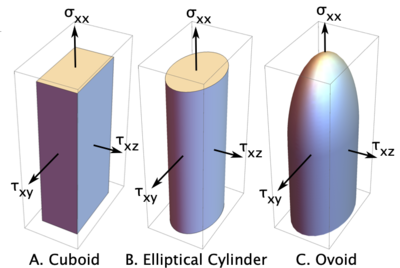
Three possible failure stress failure surfaces are shown in the figure. Which surface to use for initiation is determined by the <tt>tractionFailureSurface</tt> property of the parent [[Isotropic Softening Material|isotropic softening material]]. The calculations for initiation transpose these surface to principle stress space and find critical stress by Mohr's circle calculations. The details are given in Ref. <ref name="dmGen"/>. | |||
These initiation calculations all the properties, in general, to depend on external parameters such as pressure, strain rate, or more. The only external dependence current modeled is to shear strength to depend on pressure. | |||
== Damage Law Properties == | == Damage Law Properties == | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 31 January 2023
Introduction
This damage initiation law predicts that failure initiates when maximum principal stress exceeds tensile strength of the material or when maximum shear stress exceeds shear strength of the material. It can also model pressure-dependent initiation stresses. Because it deals with principal stresses and tensile failure is the same regardless of direction, this law is only appropriate for isotropic materials such as an IsoSoftening material.
Failure Surface
Three possible failure stress failure surfaces are shown in the figure. Which surface to use for initiation is determined by the tractionFailureSurface property of the parent isotropic softening material. The calculations for initiation transpose these surface to principle stress space and find critical stress by Mohr's circle calculations. The details are given in Ref. [1].
These initiation calculations all the properties, in general, to depend on external parameters such as pressure, strain rate, or more. The only external dependence current modeled is to shear strength to depend on pressure.
Damage Law Properties
The following table lists the input properties for maximum principal stress failure surface:
| Property | Description | Units | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| sigmac | Critical tensile stress for failure | pressure units | infinite |
| tauc | Critical shear stress for failure | pressure units | infinite |
References
- ↑ J. A. Nairn, "Generalization of Anisotropic Damage Mechanics Modeling in the Material Point Method," Int. J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, in press (2022).